Security controls are the measures taken to safeguard an information system from attacks against the CIA of the information system.
Security controls are selected and applied based on a risk assessment of the information system.
The risk assessment process identifies systems threats and vulnerabilities, and then security controls are selected to reduce or mitigate risk.
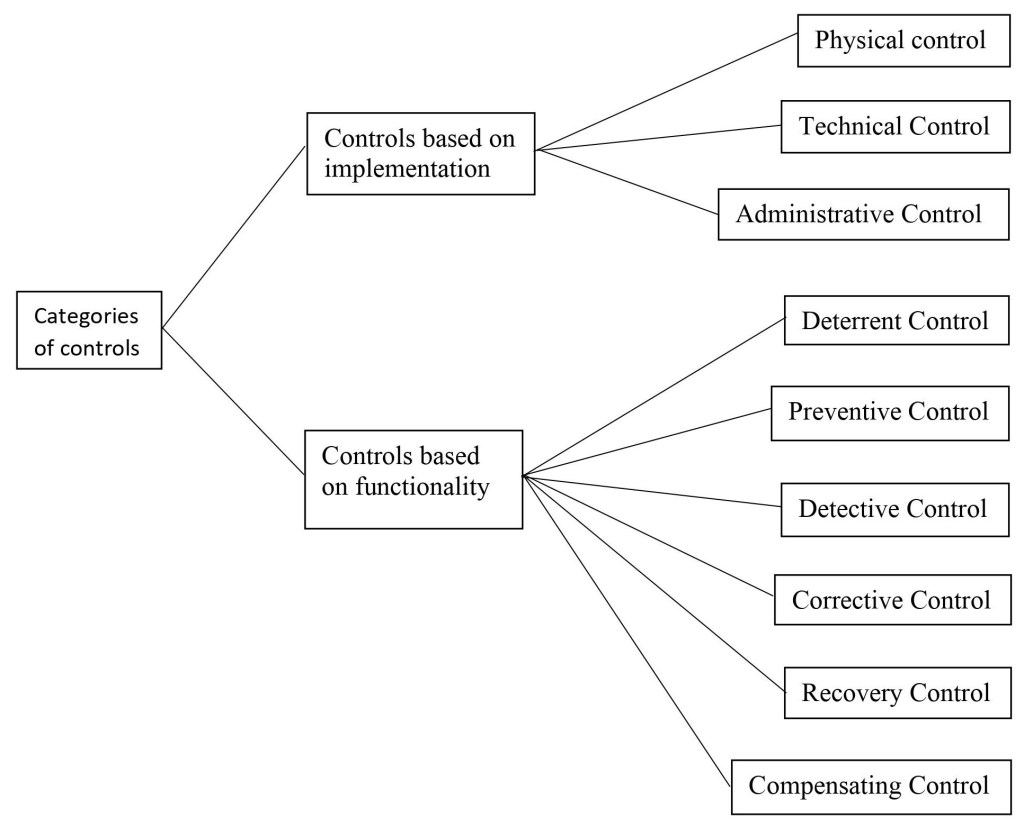
Components based on Implementation
| Administrative Controls | Technical Controls | Physical Controls |
| They are commonly referred as soft controls, because they are more management oriented. | Technical controls are also called logical controls, are software or hardware components. | They are items put into place to protect facility, personnel, and resources. |
| For example: Security documentation, Risk management, Personnel security and training. | For example : Firewall and IDS, encryption, identification and authentication mechanisms. | For example : Security guards, locks and fencing. |
Components based on Functionality
| Deterrent | Preventive | Corrective |
| Intends to discourage a potential attacker | Intends to avoid an incident from occurring | Fixes components or systems after an incident occur |
| Recovery | Detective | Compensating |
| Intends to bring the environment back to regular operations | Helps identify an incident’s activities and potentially an intruder | Provides an alternative measure of control |
Control Framework
- Control Framework is a data structure that comprises a set of an organization’s internal controls that are the practices and strategies built to enhance business processes and minimize risk.
- It is a set of controls that protects data within the IT infrastructure of a business or another entity.
- The control framework acts as a comprehensive security protocol that protects against fraud or theft from a spectrum of outside parties, including hackers and other kinds of cyber criminals.

Example of a control framework : COBIT
COBIT(Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies)
Main function is to help the company map their IT process to ISACA best practices and standards.
COBIT Priniciples:
- Meet Stakeholder needs
- Covering the enterprise end-to-end
- Applying a single integrated framework
- Enabling a holistic approach
- Separating governance from management
Discover more from Information Security Blogs
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
