Goals, Mission and Objectives
Goals: Define what the organization desires to achieve
Goals provide the overall context of what the organization wants to accomplish.
Mission: Indicate how will you proceed to them
Mission is a statement of the organization’s purpose and reason for existence.
Objectives: Help in creation of long term and short term strategies
Objectives are milestones or specific results that are expected and help to reach the goals of the organization.
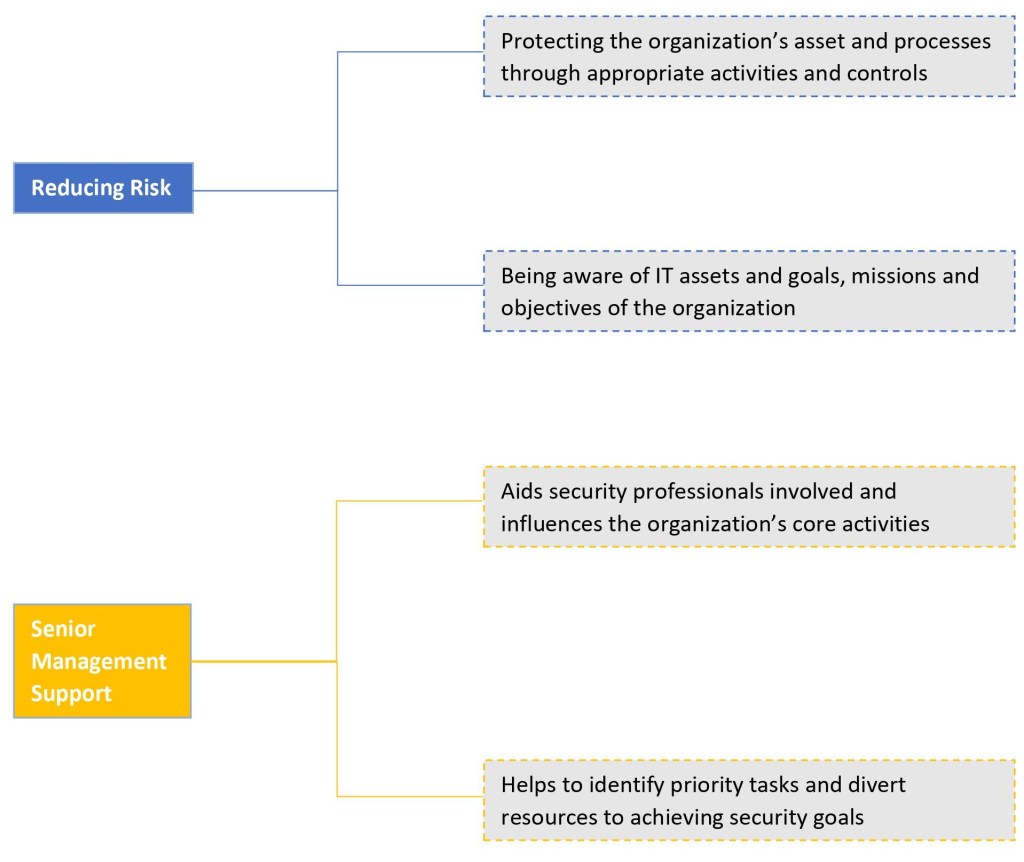
Aligning Security with Goals, Mission and Objectives
Information Security can be aligned with organizational goals, missions and objectives in two ways.
Due Care
It is a legal term that pertains to the legal duty of the organization. Lack of due care is considered negligence.
Due care shows that company has:
- Taken responsibility for the activities that taken place within the corporation
- Taken necessary steps to protect the company, its resources and employees from possible threats
- Take reasonable care in protection of organization.
Examples:
- Training employees in security awareness
- Mandating statements from the employees stating that they have read and understood appropriate computer behavior
- Deploying firewalls in organization
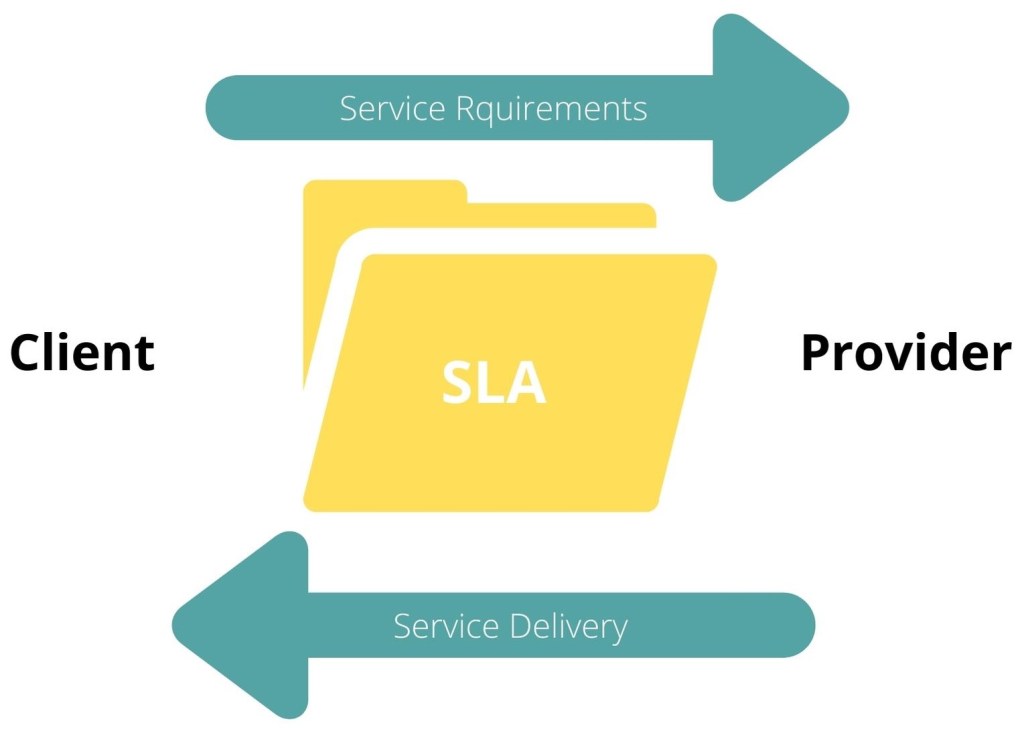
Service-Level Agreement(SLA)
SLA is a formally defined level of service provided by an organization.
SLA may be defined for:
- Security incident Response
- Security Alert Delivery
- Security Investigation
- Policy and procedure review
Managing Third-Party Governance
Outsourcing is the subcontracting of a business process to a third-party company.
Risk associated with outsourcing:
- Loss of control of confidential information
- Accountability
- Compliance
Secure Outsourcing
- On-site assessment
- Document exchange and review
- Policy and process review
Offshoring: Privacy Requirements and Compliance
Offshoring is outsourcing to another country.
- Offshoring can increase privacy and regulatory issues.
- For example: Data offshored to India by U.K. Medical organization has no HIPAA certification.
- A good contract ensures that regulations and laws governing privacy are followed, even beyond the country’s jurisdiction.
- For example: The Indian company to which the U.K. medical organization’s data is offshored can agree to follow HIPAA via contract.
Security management plan
It is the identification of an organization’s asset followed by development, documentation and implementation of policies and procedures for protecting these assets.
Characteristics:
- Senior management is responsible for initiating and defining policies.
- Middle management is responsible for releasing standards, baselines and guidelines in relation to the policies.
- Operations management or IT teams implement the controls defined above.
- End-users must comply with all the functions of the organization
- It should have approval from senior management before engagement
Types of Security Management Plan
| Strategic Plan | Tactical Plan | Operational Plan |
| Its a long term plan | Its a mid term plan developed to provide more detailed goals | It is a short term but highly detailed plan |
| Useful for at least 5 years and reviewed annually | Last usually for a year or 2 | Must be updated often |
| Helps to understand the security functions and aligns with business | Is more technology oriented | Spells how to accomplish various goals |
| Defines organization’s security posture | Example: Project plan. budget plan, etc. | Example: Resource allotment, training plans, etc. |
| Should include risk assessment |
These 3 plans combined together is called planning horizon,
Discover more from Information Security Blogs
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
