Security policy is a broad statement produced by the senior management that dictates the role of security within the organization.
Characteristics of Security Policy
- It must be generic, non technical, and easily understood
- It must integrate security into all business processes and functions
- It must be reviewed and modified periodically or as the company environment changes
- It must support the vision and mission of the organization
Types of security policies:
- Organizational security policy: It focuses on issues relevant to every aspect of the organization
- Issue specific policy : It focuses on a specific service, department, or function that is distinct from the organization as a whole
- System specific policy : It focuses on individual systems
Different security policies work together to meet the objectives of a comprehensive security program.
- Regulatory Policy: Regulatory policy ensures that the organization is following industry specific regulations or standards. Example: HIPPA, PCI DSS, etc.
- Advisory Policy: Advisory policy strongly advises the employees or users on the type of behaviors and activities to be followed within the organization. Example: Policy for handling medical or personal information
- Informative Policy: Informative policy informs the employees of certain key topics. Example: Policy explaining the goals and mission of an organization
Security Policy Implementation
Policy documents often come with the endorsement or signature of the executive powers within an organization.
- Standard policy components : Purpose statement, policy objectives, resources provision, staff allocation, and guidelines and standards
- Policy elements : Purpose, scope, responsibilities, and compliance
- Policy creation guidelines: Assigning a principal function to be responsible for control, compliance with policy as a condition of employment, and avoiding exceeding two pages and use generic terms
- Management responsibilities for policy: Protecting resource assets within the company’s control, implementing security in accordance with the company policy, and initiating corrective actions for security violations
- Policy enforcement: Avoiding errors that can lead to legal challenges and ensuring compliance with policy
Policy Chart
A strategic goal can be viewed as the ultimate endpoint, while tactical goals are the steps necessary to achieve it.
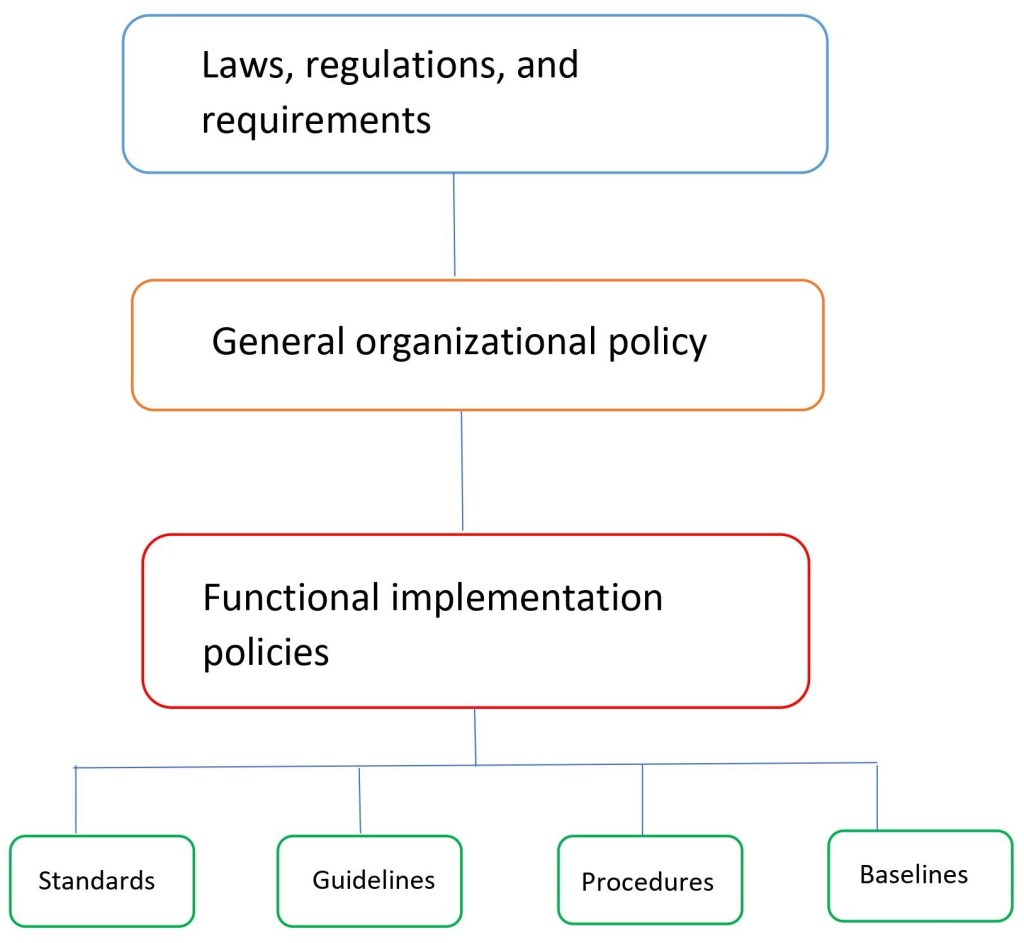
Standards
- Refer to the mandatory activities, rules, actions, or regulations
- Example: ISO 27001
Guidelines
- Refer to the recommended operational guides or actions provided to the users operations staff, IT staff, and others
- Example: Security Password Guideline
Procedures:
- Refer to the step by step tasks to be performed to achieve a certain objective
- Example: Incident response procedure
Baselines:
- Define minimum level of security that every system must meet
- Example: All Windows 7 systems must have SP1 installed
Discover more from Information Security Blogs
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
