Hey, I have just started learning about the AWS cloud service. During, my whole learning period I will be going to upload my notes or learnings over these blogs for others too.
Traditional IT Approach
How websites work

We have a server that is hosted somewhere and the client uses a web browser to get access to the server to view the website
To connect the client and server we are going to use the network or internet.
Now, for clients to identify server and server to identify clients we are going to use their IP addresses.
What does a server contain?
- CPU to compute
- RAM for memory
- Storage for storing data
- Database to store data in structured way
- Networking for connectivity
Nowadays, there are a number of problems with this approach:
- Pay for rent of data center
- Pay for power supply
- Maintenance of servers
- Scalability
- Monitoring
- Dealing during disasters and pandemics
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of compute power, database storage, applications, and other IT resources with pay-as-you-go pricing.
Types of cloud:
- Private Cloud:
- Cloud services used by single organization, not exposed to public
- Complete control
- Security for sensitive applications
- Public Cloud:
- Cloud resources owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider delivered over internet
- Hybrid Cloud:
- Keeps some servers on premises and extend some capabilities to cloud
The Five Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- On-demand self-service:
- Users can provision resources and use them without human interaction from the service provider
- Broad network access:
- Resources available over the network, and can be accessed by diverse client platforms
- Multi-tenancy and resource pooling:
- Multiple customers can share the same infrastructure and applications with security and privacy
- Multiple customers are serviced from the same physical resources
- Rapid elasticity and scalability:
- Automatically and quickly acquire and dispose resources when needed
- Quickly and easily scale based on demand
- Measured service:
- Usage is measured, users pay correctly for what they have used
Six Advantages of Cloud Computing
- Trade capital expense (CAPEX) for operational expense (OPEX)
- Pay On-Demand: don’t own hardware
- Reduced Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) & Operational Expense (OPEX)
- Benefit from massive economies of scale
- Prices are reduced as AWS is more efficient due to large scale
- Stop guessing capacity
- Scale based on actual measured usage
- Increase speed and agility
- Stop spending money running and maintaining data centres
- Go global in minutes: leverage the AWS global infrastructure
Problems solved by the Cloud
- Flexibility: change resource types when needed
- Cost-Effectiveness: pay as you go, for what you use
- Scalability: accommodate larger loads by making hardware stronger or adding additional nodes
- Elasticity: ability to scale out and scale-in when needed
- High-availability and fault-tolerance: build across data centres
- Agility: rapidly develop, test and launch software applications
Types of Cloud Computing
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
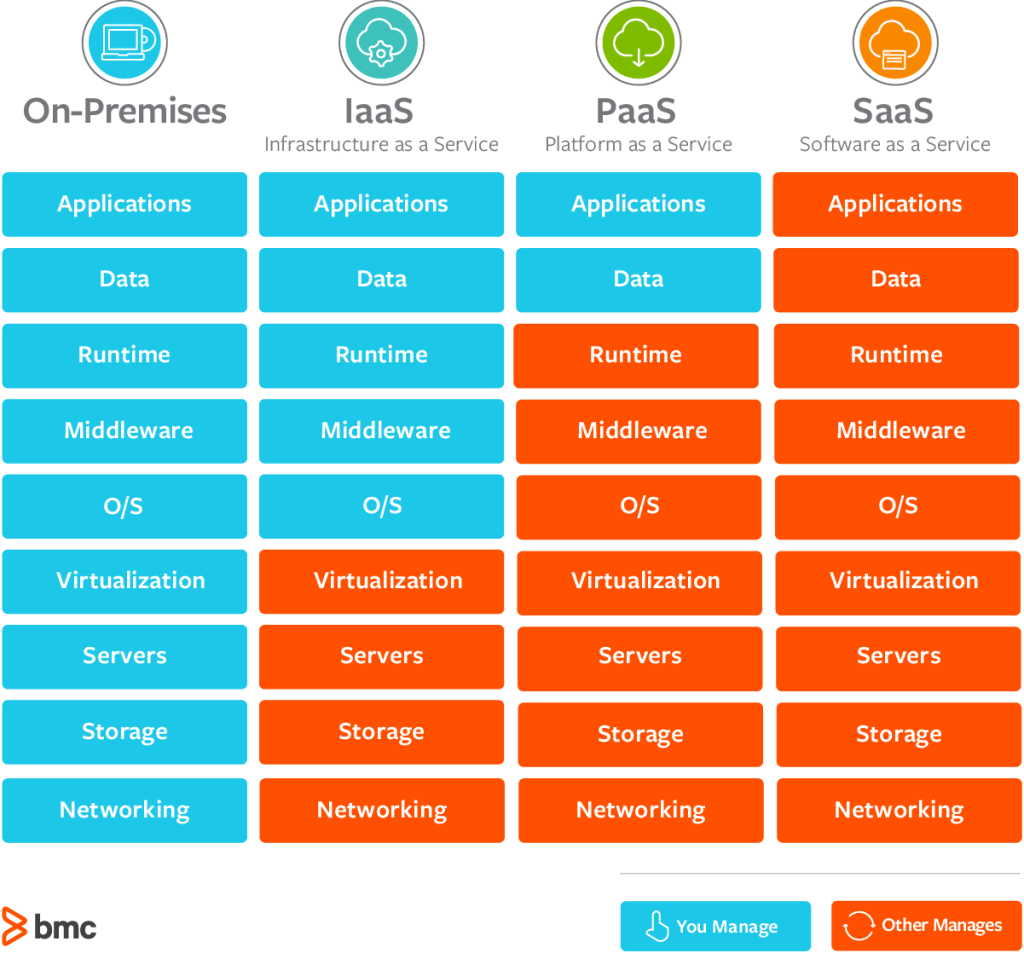
Pricing of the Cloud – Quick Overview
AWS has 3 pricing fundamentals, following the pay-as-you-go pricing model
- Compute:
- Pay for compute time
- Storage:
- Pay for data stored in the Cloud
- Data transfer OUT of the Cloud:
- Incoming data transfer is free
Shared Responsibility Model
It is a diagram that defined what are responsibilities will be taken care of by AWS versus what will be managed by you/customer/end-user.
Discover more from Information Security Blogs
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
