Objectives of the Stage 1 Audit
- To audit the auditee’s management system documentation
- To evaluate the auditee’s location and site-specific
- To determine the preparedness for the stage 2 audit
- To review the auditee’s status and understanding regarding requirements of the standard
- To collect necessary information for the planning of the stage 2 audit
- To agree with the auditee on the details of the stage 2 audit
- To evaluate if the internal audits and management review are being planned and performed
Stage 1 Audit steps
Site Visit
Activities To be Carried Out
- Evaluation of the location and site-specific conditions of the audit
- Contacts with the personnel of the auditee
- Observation of the technologies used
- General observation of the operations of the management system
Document review
The main objectives of the document audit are:
• General understanding of the operation of the management system
• Evaluation of the design of the management system as well as the related processes and controls
• Verification that internal audits and management reviews have been conducted
Types of Documents to be Audited
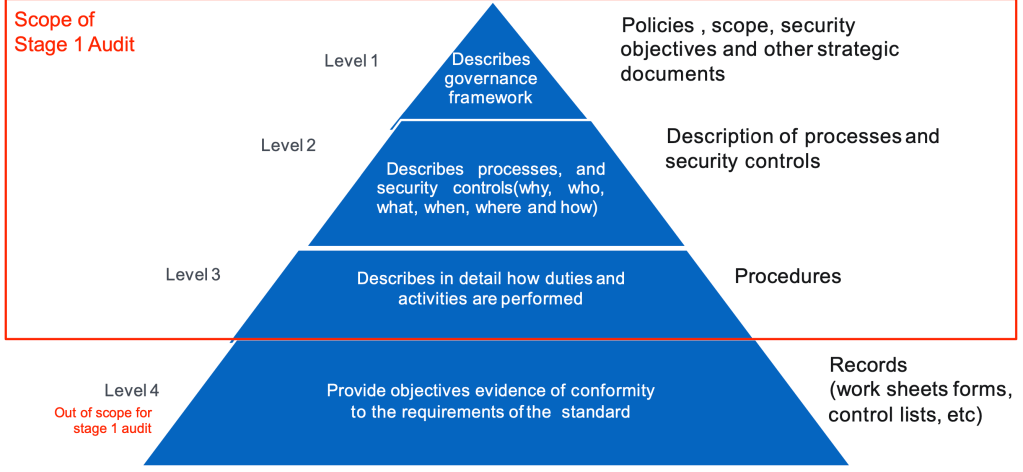
Evidence Collection and Analysis Procedures
- Observation
- Document Review
- Interview
- Analysis
- Technical verification
- Corroboration
- Evaluation
A. Audit Procedure: Observation
Direct observation is one where the auditor observes a phenomenon based on his senses without wanting to modify them with appropriate procedures. For example, the auditor observes:
- Flow of a software update process
- Employee performance
- Inventory of computers
- Presence of a fire prevention device
B. Audit Procedure: Document Review
The document review consists of a systematic and methodical review of text documents
The auditor must evaluate the conformity of the documents in terms of:
- Content
- Format
- Document management procedure
C. Audit Procedure: Interview
Discussion/interview:Ask employees and other interested persons (third parties) questions (verbal or written) to gather audit evidence. To be efficient, an interviewer shall:
- Avoid influencing information
- Take notes rapidly
- Corroborate the information whenever possible
D. Audit Procedure: Analysis
An analysis consists in a systematic and methodical analysis of data or information to identify, determine and analyze relationships or tendencies.
E. Audit Procedure: Technical Verification
To validate the effectiveness of a technical process or control, the auditor can ask to be present for a complete process that is:
▪ Analysis of configurations
▪ Real-time operation (or simulation)
▪ Scanning
• For example, be present for the restoration of a backup
The auditor must never perform the operations linked to a test and must be careful to limit impacts on the organization.
F. Audit Procedure: Corroboration
Corroborating is verifying information to get a reasonable level of assurance. The auditor can:
- Ask different people the same questions and compare their answers.
- Compare interview responses to documentation
- Compare documents or interview notes against direct observations.
- Request corroboration of facts from an external source such as a client or supplier
G. Audit Procedure: Evaluation
- Evaluating is the act by which the auditor judges the results of the previous procedures to ensure that the evidence is sufficient, relevant and reliable
- The auditor shall evaluate the quantity and quality of the information: If there is relevant, reliable and enough evidence to have a reasonable assurance
- Audit evidence should be evaluated against the audit criteria to generate the audit findings.
Stage 1 Audit Report
Stage 1 audit findings shall be documented and communicated to the auditee and the audit client, including identification of any areas of concern that could be classified as a non-conformity during the stage 2 audit.
Discover more from Information Security Blogs
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
