Objectives of Stage 2 Audit
- Conducting the opening meeting
- Collecting Information
- Drafting of audit findings and non-conformity reports
- Quality review of the audit findings
Step 1 Conducting the opening meeting
ISO 19011, Clause 6.4.3
The purpose of the opening is to:
- confirm the agreement of all parties (e.g. auditee, audit team) to the audit plan
- Introduce the audit team
- Ensure that all planned audit activities can be performed.
Step 2 Collecting Information
Information can be collected in the form of:
- Records
- Documents
- Interviews
- Observation
- Databases
and many more…
Audit Procedure – Interview
Ask employees and other interested persons (third parties) questions (verbal or written) to gather audit evidence.
The auditor shall chiefly use open-ended questions such as:
- Who, what, where, why, when, how?
- Show me …, tell me …, explain to me…
The auditor should avoid:
- Close-ended question (yes/no answers)
- Guided questions
Close-ended question can be used to open a topic, then followed by open questions Ex: Do you have any ISMS policy? Tel me…
After the Interview
- Complete the work documents before going on to another task
- Send a thank you email to the interviewee with a summary of the interview including the list of the documents and actions to be provided by the interviewee WITH a dude date
- Follow-up on the items agreed to during the interview
Step 3 Drafting of Audit Findings and Non-conformity Reports
• It is appropriate to evaluate audit evidence against the audit criteria to develop audit findings.
• Audit findings may indicate conformity, non-conformity and opportunities for improvement or good practices
Audit Findings – Definition
ISO 19011, Terms and definitions: 3.10
- Results of the evaluation of the collected audit evidence against criteria
- Note: Audit findings may indicate conformity or non-conformity or may lead to the identification of opportunities for improvement
Types of audit findings
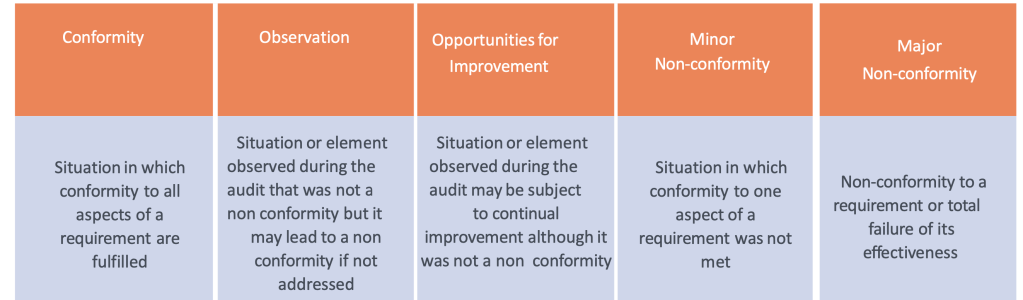
Non-conformity
Definition
- According to the definition of the ISO 9000: 2005 (clause 3.6.2) standard, a non- conformity is the “non-fulfilment of a requirement”
- There are two types of non-conformities
- Minor non-conformity
- Major non-conformity
Drafting a Non-conformity Report
- If an audit finding is a non-conformity, the auditor must document it in a non- conformity report
- Adequate documentation of a non-conformity includes 3 items:
- Description of the requirements for which the non-conformity was detected (audit criteria)
- Description of the observed non-conformity (evidence supporting the findings)
- Non-conformity type (minor or major)
Discover more from Information Security Blogs
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
