Information Security Management
Information security is the process of protecting information and information systems from the following:
- Unauthorized disclosure, access and use
- Destruction
- Deletion
- Modification
- Disruption
Factors that impact information security
- Technology
- Platforms and tool used
- Network Connectivity
- Level of IT complexity
- New or emerging security tools
- Operational support for security
- Business Plan and Environment
- Nature of Business
- Risk Tolerance
- Industry Trends
- Merger acquisitions and partnership
- Outsourcing service or providers
What is cybersecurity?
- Cyber security refers to anything intended to protect enterprises from intentional attacks, breaches, incidents and consequences.
- It can also be defined as protection of information assets by addressing threats to information processed, stored and transported by internetworked information systems.
Importance of cyber security
- Elimination of cyber crime
- Protection of business data
- Control of cyber crime syndicates
- Existence of cyber armies
- Reduction of financial fraud
Information Security v/s Cyber Security
| Information Security | Cyber Security |
| Information Security deals with information, regardless of its format. It encompasses paper, documents, digital data and intellectual property. | It can also be defined as protection of information assets by addressing threats to information processed, stored and transported by internetworked information systems. |
| Cyber Security is a component of information security. |
Approaches for cyber security
- Compliance Based Security : This approach relies on regulations or standards to determine security implementation.
- Risk Based : This approach relies on identifying the unique risk a particular organization faces and designing and implementing security controls to address that risk.
- Ad-Hoc : An Ad-Hoc approach simply implements security with no particular criteria.
CIA Triad
Confidentiality(C), Integrity(I) and Availability(A) are three basic principals of security.
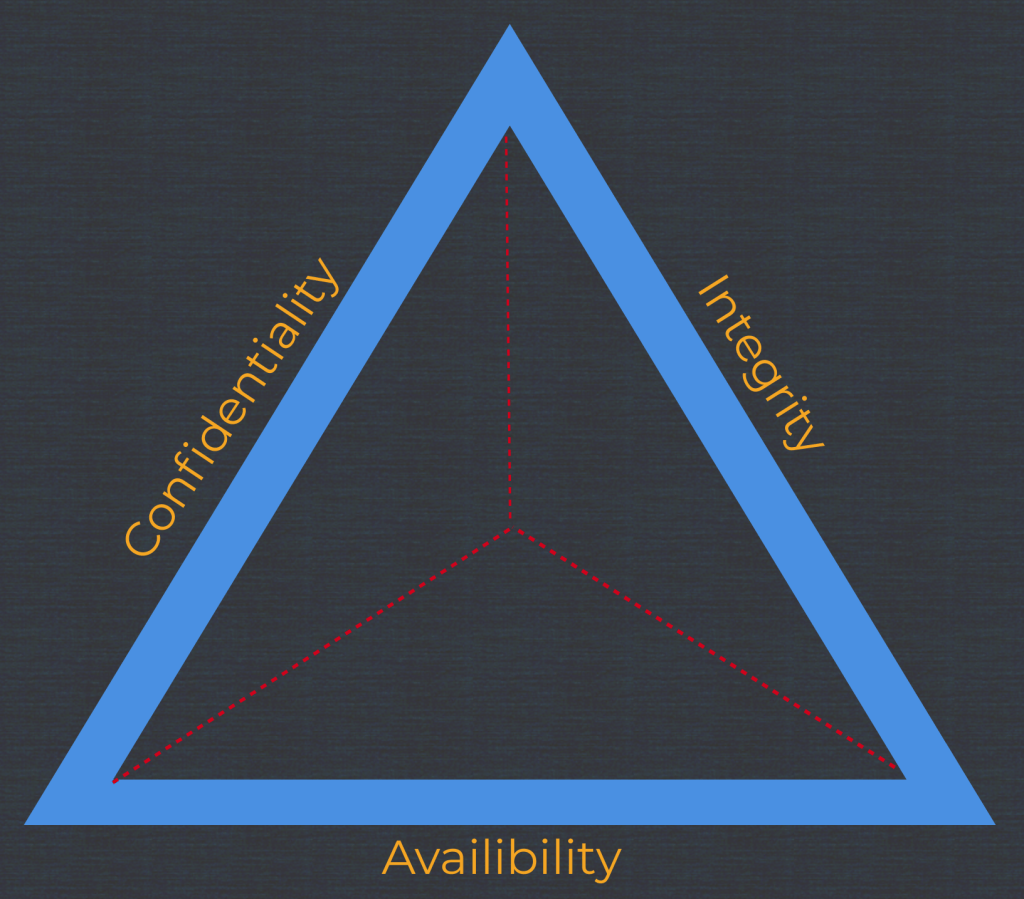
Confidentiality
The principal of confidentiality states that information and functions can be accessed by authorized parties.
Threats to confidentiality
- Hackers
- Masqueraders
- Unauthorized user activity
- Unprotected files download
- Unprotected Networks
- Unauthorized Programs
- Social Engineering Attacks
Integrity
The principal of integrity states that information and functions can be added, altered or removed only by authorized people and means.
Threats to integrity
- Hackers
- Masqueraders
- Unauthorized user activity
- Unprotected files download
- Unprotected Networks
- Unauthorized Programs
- Social Engineering Attacks
- Authorized subject corrupting data and programs accidentally or intentionally
Availability
This principal states that systems, functions and data must be available on-demand according to agreed upon parameters based on levels of service.
Threats to availability
- DoS
- DDoS
- Natural Disasters
- Man Made Disasters
Definitions
- Asset : Something of either tangible or intangible value that is worth protecting, including people, information, infrastructure, finance and reputation
- Vulnerability : It is a lack of a countermeasure or a weakness in a countermeasure that is in place.
- Threat : It is any potential danger that is associated with the exploitation of a vulnerability.
- Threat Agent : The entity that takes advantage of vulnerability.
- Risk : It is the likelihood of a threat agent exploiting a vulnerability and the corresponding business impact.
- Control or counter-measure : It is put into place to mitigate the potential risk.
Example: Case Study
If a company has anti-malware solution, but does not keep the signatures up-to-date, this is a vulnerability.
The company is vulnerable to malware attacks.
The threat is that a virus will show up in the environment and disrupt productivity.
Apply the right countermeasure can eliminate the vulnerability and exposure, and thus reduce the risks.
The company cannot eliminate the threat agent, but it can protect itself and prevent this threat agent from exploiting vulnerabilities within the environment.